
Cotton swabs pushed into the ear might compress earwax and push it more profound within the ear, resulting in a blockage.Ĭholesteatomas: A cholesteatoma is a benign growth that can form in the ear canal. Cotton swab usage can sometimes cause this. Individuals who generally work outside and invest most of their time outside are at risk of contracting the infection.Įarwax Blockage: If there is enough earwax in the ear canal, it might clog it. This is the popular name for the possibility of a swimmer getting an ear canal infection. Swimmer's Ear: It might cause enlargement of the ear canal. Allergic rhinitis, food allergies, and allergies to substances like hair spray, for example, can cause itching in the ears.
#Auditory canal skin#
Ear eczema can produce flaky, dry skin as well as swelling around the ear canal.Īllergies: Allergies can cause itchy ears in some people. Eczema is an assemblage disease related to skin that creates inflamed, itchy areas. Skin Conditions: Psoriasis and eczema are two skin diseases that can damage the ear. Various factors that can cause itchy ears are as follows: Although individuals may find it annoying, this symptom usually does not signal a significant condition. Many individuals have itching ears at some time in their lives.

There are some allergies and conditions related external auditory canal that are very common. It mainly influences children (aged between 3 months to 3 years) and is usually caused by bacterial infection. Otitis medium (inflammation of the middle ear) is the most prevalent disease involving the tympanic membrane. Therefore, it is used to diagnose middle-ear disorders accurately. The mobility or appearance of the tympanic membrane is typically pearl grey but can be tinted with yellow or pink. The membrane is rich in sensory nerve fibers and blood vessels, making it sensitive to discomfort or pain. The tympanic membrane is made up of three layers:Īn exterior layer that connects to the skin on the external canal.Īn inside layer that connects to the lining of the mucous membrane in the middle ear.Ī layer of circular and radial fibers provides tension and rigidity to the membrane. The margins are connected to the tympanic annulus, a bone ring. The eardrum is flattened shaped like a cone with its tip pointing inbound and expanding the external canal. The external auditory canal is separated by auditory ossicles that are structured as the lateral wall in a cavity. Auditory ossicles are minor bones in the eardrum cavity. A thin membrane in the mammal's ear collects and transfers sounds from the surrounding air to the auditory ossicles. The eardrum is the common name of the tympanic membrane. The isthmus, which connects the cartilaginous and bony parts of the auditory canal, is the tapered point of the canal. Thus, this joint is also known as the foramen of Huschke. The foramen tympanicum in the front and below the osseous portion is a variation defect that communicates with the temporomandibular joint. There is no subcutaneous tissue in a particular region therefore, the skin is directly placed to the periosteum. The squamous portion gives birth to the upper part and roof of the posterior wall of the temporal bone.
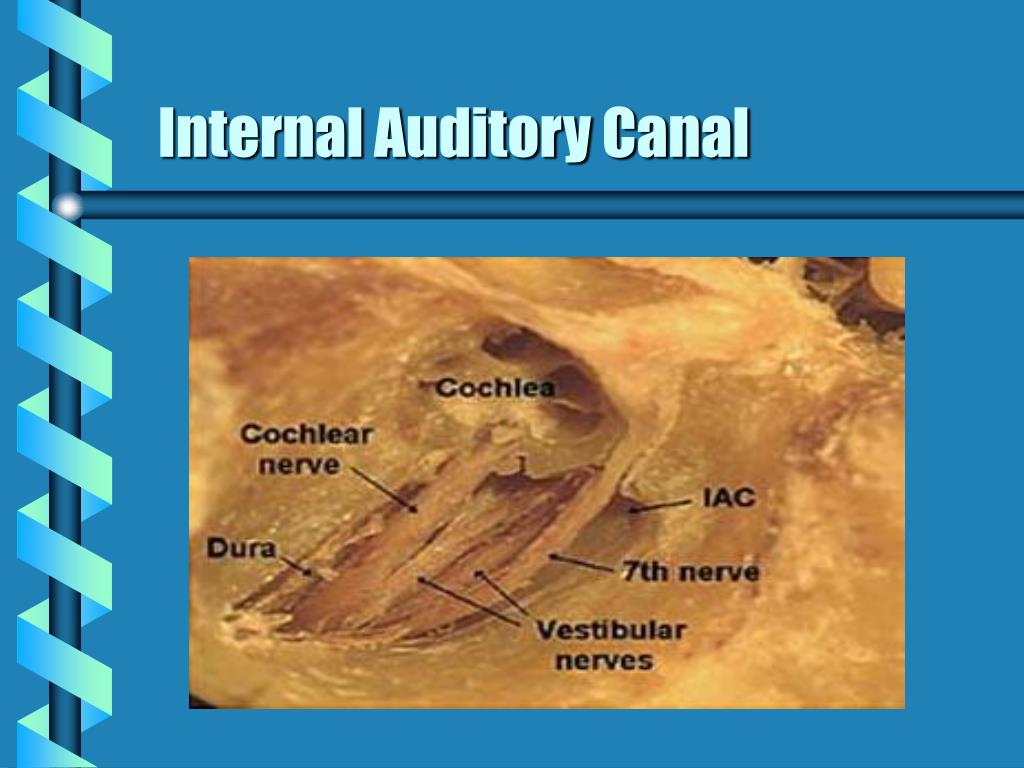
The tympanic area of the temporal bone starts to the anterior floor, wall, and lower portion of the back wall. Bone surrounds the medial two-thirds of the spine. Fissures of Santorini are a flaw in the cartilaginous portion that allows disease and cancer to spread. A fibrocartilaginous tube that runs parallel to the auricle defines the lateral one-third. It resembles a slightly curved tube that runs inward from the auricle's floor, or protruding region of the outer ear, and stops blindly at the eardrum membrane, which divides it from the middle ear. It is usually two and a half centimeters long and structured like the letter "S".
In all animals, the external auditory canal has similar anatomy.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
